Fatty Liver Disease: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Fatty liver disease is a condition where excess fat gradually accumulates in the liver, affecting its normal functioning. With modern lifestyles becoming more sedentary and diets increasingly processed, this condition is now being diagnosed more frequently across all age groups. What makes fatty liver disease concerning is that it often develops quietly, without early warning signs.
The good news is that with early detection and the right fatty liver disease treatment, liver damage can often be controlled and even reversed. Understanding how the condition develops, what symptoms to look for, and how it is treated plays a crucial role in long-term liver health.

Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
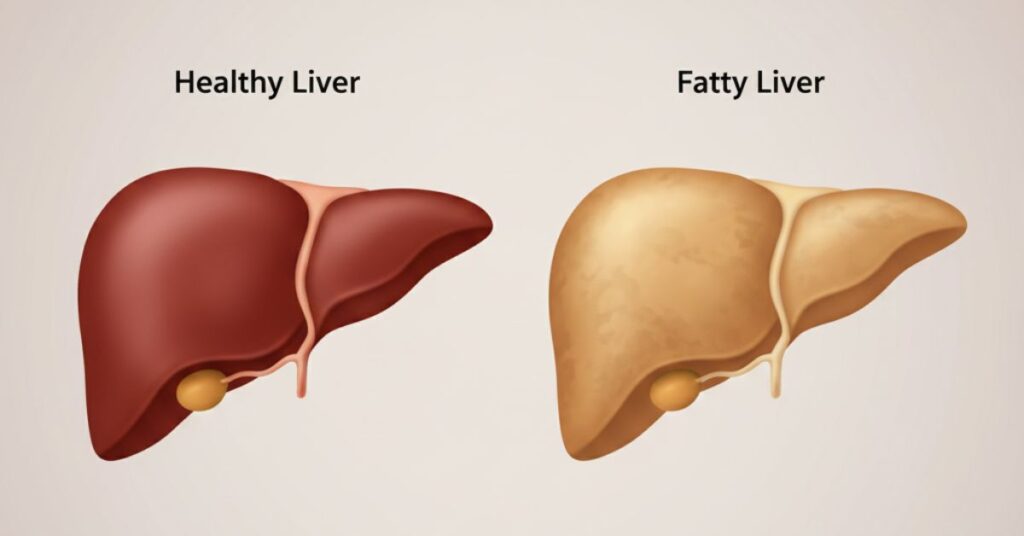
The liver normally contains a small amount of fat. Problems arise when fat accumulation increases beyond healthy limits and begins to interfere with liver functions such as metabolism, detoxification, and digestion.
Fatty liver disease is broadly classified into two categories. One form develops in individuals who drink little or no alcohol, while the other is linked to prolonged or excessive alcohol intake. Although the causes differ, both forms require medical attention to prevent progression.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
In its early stages, fatty liver disease may not cause noticeable discomfort. Many individuals remain unaware of the condition until routine health tests reveal abnormal liver readings. As the condition advances, some people may experience:
- Constant tiredness or low energy levels
- A feeling of heaviness or mild pain in the upper right abdomen
- Reduced appetite
- Nausea without a clear cause
- Unexplained changes in weight
- Altered liver enzyme levels in blood tests
Because these symptoms can be subtle, regular health check-ups are important, especially for people at higher risk.
What Leads to Fat Accumulation in the Liver?
Fatty liver disease develops due to a combination of lifestyle, metabolic, and health-related factors. Common contributors include:
Poor Dietary Habits
Frequent consumption of high-calorie foods, excess sugar, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats places extra strain on the liver, encouraging fat storage.
Excess Body Weight
Being overweight, particularly carrying fat around the abdomen, significantly increases the likelihood of liver fat buildup.
Metabolic Disorders
Conditions such as type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance affect how the body processes fats, leading to increased fat deposition in liver cells.
Elevated Blood Lipids
High cholesterol and triglyceride levels can contribute to fat accumulation within the liver.
Alcohol Consumption
Regular or heavy alcohol intake disrupts normal liver metabolism and promotes fat buildup, especially when combined with poor nutrition.
Limited Physical Movement
A routine lacking regular physical activity reduces calorie utilization and slows metabolic processes, allowing excess fat to settle in the liver.
Identifying the underlying cause is essential for selecting the most effective fatty liver disease treatment approach.
Why Early Treatment Matters
Ignoring fatty liver disease can lead to progressive liver damage over time. Without proper management, fat accumulation may trigger inflammation and scarring of liver tissue. In advanced stages, this can impair liver function and increase the risk of serious complications.
Early medical intervention significantly lowers these risks and supports liver recovery before permanent damage occurs.
How Fatty Liver Disease Is Diagnosed
Doctors usually diagnose fatty liver disease through a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests. These may include:
- Blood tests to assess liver enzyme levels
- Imaging studies such as ultrasound
- Review of medical history and lifestyle factors
- Physical examination
Accurate diagnosis helps determine disease severity and guides the treatment plan.
Fatty Liver Disease Treatment Options
There is no instant cure for fatty liver disease. Treatment focuses on reducing liver fat, improving metabolic health, and preventing disease progression.
Lifestyle-Based Treatment
Lifestyle improvement is the cornerstone of fatty liver disease treatment. Key steps include:
- Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet
- Reducing intake of processed and sugary foods
- Achieving gradual, sustainable weight loss
- Incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines
Even modest lifestyle changes can lead to noticeable improvement in liver health.

Medical Support
While no specific medication directly eliminates liver fat, doctors may prescribe treatment to control related conditions such as diabetes, cholesterol imbalance, or metabolic disorders. Managing these conditions reduces liver stress and supports recovery.
Alcohol Management
For individuals with alcohol-related liver fat, reducing or completely stopping alcohol intake is essential for healing and preventing further damage.
Ongoing Monitoring
Fatty liver disease improves gradually. Regular follow-up visits help:
- Track liver enzyme changes
- Monitor response to treatment
- Adjust lifestyle or medical plans as needed
Consistent monitoring ensures long-term liver protection.

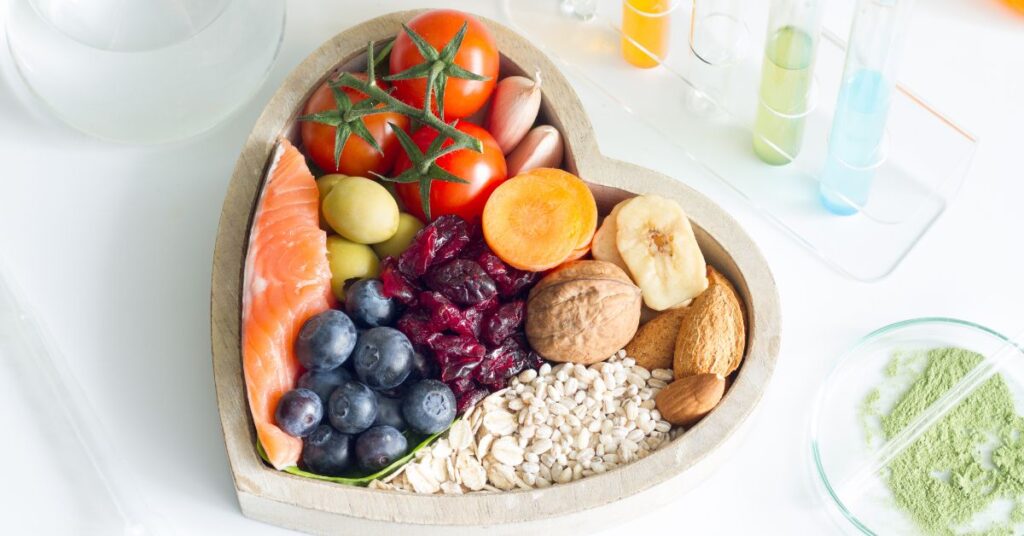
Diet and Liver Health
Diet plays a central role in fatty liver disease treatment. A liver-friendly eating pattern typically includes:
- Fresh vegetables and fruits
- Whole grains
- Lean protein sources
- Healthy fats in controlled amounts
Avoiding excess sugar, refined flour, and fried foods allows the liver time to recover and function efficiently.

Role of Physical Activity
Physical movement helps the body use stored fat more effectively. Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity, supports weight management, and reduces liver fat. Simple activities such as walking, stretching, or light workouts can make a significant difference when practiced consistently.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Medical consultation is advised if:
- Liver test results remain abnormal
- Persistent fatigue or abdominal discomfort is present
- There is a history of diabetes, obesity, or lipid disorders
- Imaging reports indicate fatty changes in the liver
Timely care allows early intervention and better outcomes.

Living Well With Fatty Liver Disease
With proper guidance, many individuals successfully manage fatty liver disease and maintain normal liver function. Commitment to lifestyle changes and regular medical follow-ups are key to long-term success.
When addressed early, fatty liver disease is often reversible.
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is increasingly common, but it is also manageable when identified early. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and available fatty liver disease treatment options empowers individuals to take control of their liver health.
Through timely diagnosis, lifestyle improvement, and medical supervision, liver function can be protected and quality of life significantly improved.
Consult a Gastroenterology Specialist
If you are experiencing digestive or liver-related concerns, consult the specialists at Aashirwad Healthcare for accurate diagnosis and personalised gastroenterology care.

